Time:2025-12-09 Views:0
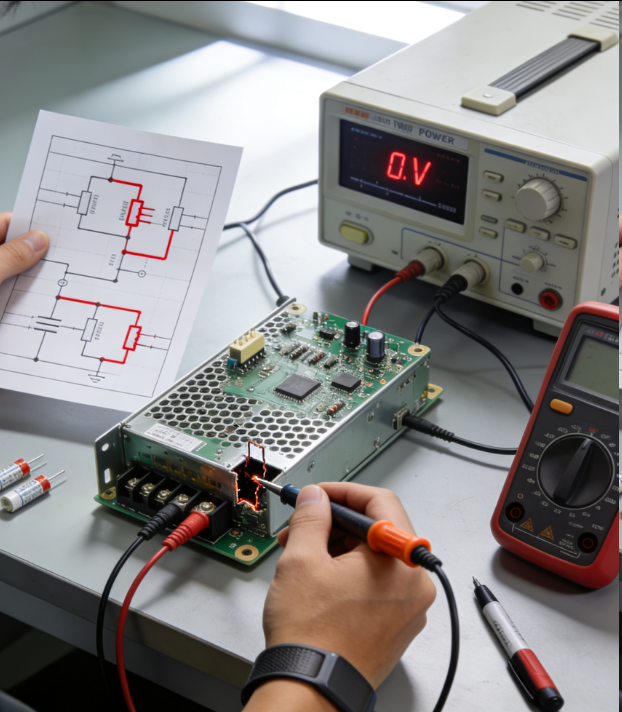
Repairing a switching power supply PCB board requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve faults efficiently. First, safety is paramount—ensure the power supply is disconnected from the mains and discharge any capacitors using a suitable resistor to avoid electric shock. Begin with a visual inspection: check for obvious signs of damage such as burnt components (like resistors, capacitors, or transistors), swollen electrolytic capacitors, broken solder joints, or traces with corrosion.
Next, use a multimeter to test key components. Measure the resistance of fuses to check if they are blown; a blown fuse often indicates a short circuit elsewhere. Test diodes (using the diode mode) to ensure they conduct in only one direction, and check transistors (both MOSFETs and BJTs) for proper functionality—look for short circuits between terminals or open circuits that suggest component failure. Capacitors can be tested for capacitance and leakage; a significant deviation from the rated value means replacement is needed.
For more complex issues, use an oscilloscope to analyze voltage waveforms at critical points, such as the input rectifier, switching transistor, and output regulator. This helps detect irregularities like unstable switching signals or insufficient output voltage. When replacing components, ensure they match the original specifications (voltage rating, current capacity, capacitance, etc.) to maintain performance and safety. Finally, after repair, perform a power - up test with a load to verify stable output voltage and current, and monitor for overheating or unusual noises to confirm the repair is successful.
Read recommendations:
33W Chinese Standard Switching power supply